Overview of Lean Manufacturing Tools:
Lean manufacturing often simply “lean“, is a systematic method for the minimization of waste within a manufacturing system without sacrificing productivity, which can cause problems. Lean also takes into account waste created through overburden and waste created through unevenness in work loads.
We are Listing the Top Lean Manufacturing Tools which we provide:-
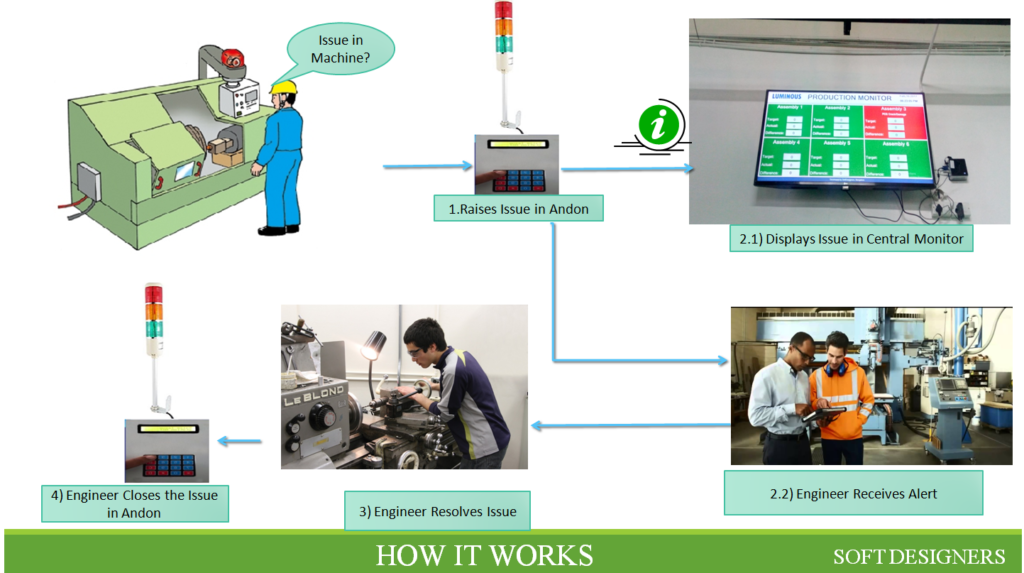
The Andon system helps the manufacturing team to know about the breakdown instantaneously which allows them to reduce the breakdown. Andon Display System provides a Visual feedback system for the plant floor that indicates production status, alerts when assistance is needed and empowers operators to stop the production process. The Andon board allows the Executives to know about the issue in a convenient manner.
The Machine status of the Factory can be learned using the Central Andon Monitor.
2. Kanban System
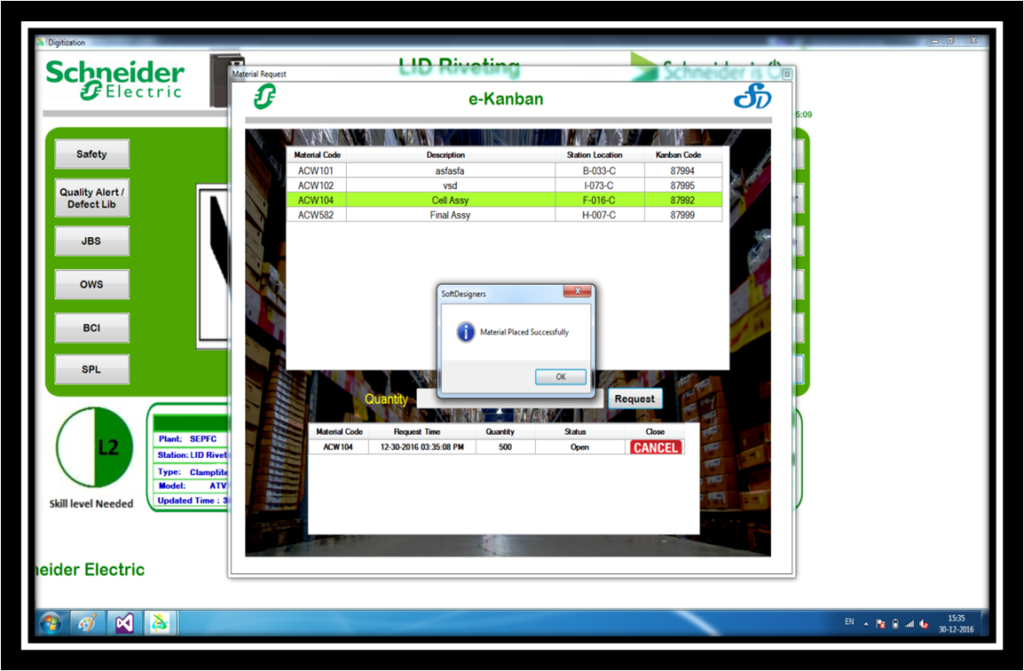
The Kanban System is an integral part of implementing the Just in Time (JIT) manufacturing philosophy ,which was designed to control inventory and reduce waste.E-Kanban is a signaling system that uses a mix of technology to trigger the movement of materials within a manufacturing or production facility.
The Kanban system combined with good inventory practices smooths out inventory levels and eliminates carrying costs.The Kanban system focuses on current conditions, production levels are calculated to take into account downtime, scrap, and changeover time of equipment to ensure that the production schedule is met.
One of the biggest advantages of the Kanban System is that it improves the responsiveness to changes in demand. In this way, the Kanban system is similar to a smart traffic light with its ability to sense when the traffic, or in this case the demand, is building up.
Another advantage of the Kanban system is that it places control in the hands of the operators who are in the best position to oversee production.
A final advantage of the Kanban system is found in the fabric of its purpose to promote an environment devoted to quality improvement. Because the Kanban system uses small lot sizes at various points in the production, quality control issues can be more easily pinpointed at the source.
3. Digitization to Standardize Work:
Gone are the days where papers are pasted around the production lines to explain the Work Instruction, Job Breakdown structure,Skill matrix,andon etc.In the 21st century we provide Digitization solution for everything in the production shop floor which will lead to more useful data available instantaneously such as Electrical drawings ,manual and so forth.
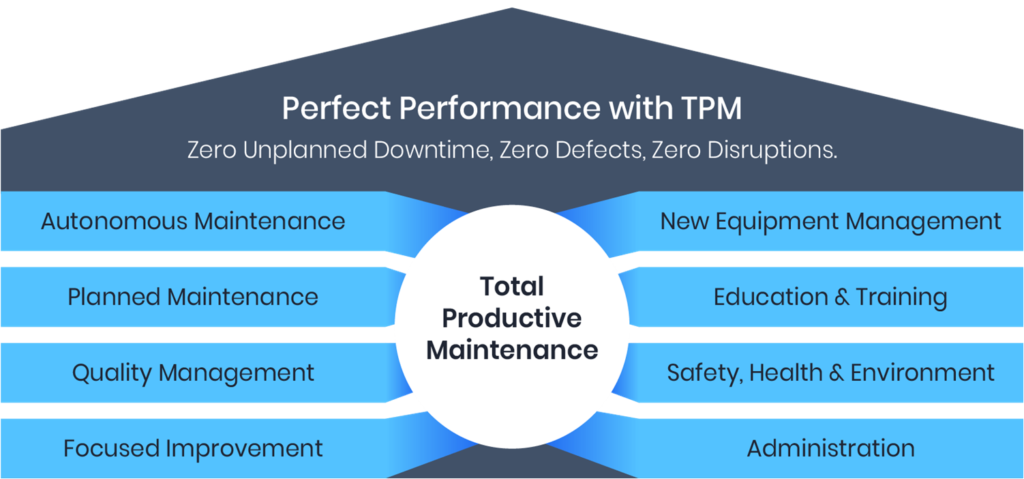
4. Total Productive Maintenance:
In industry, total productive maintenance (TPM) is a system of maintaining and improving the integrity of production and quality systems through the machines, equipment, processes, and employees that add business value to an organization.
TPM focuses on keeping all equipment in top working condition to avoid breakdowns and delays in manufacturing processes
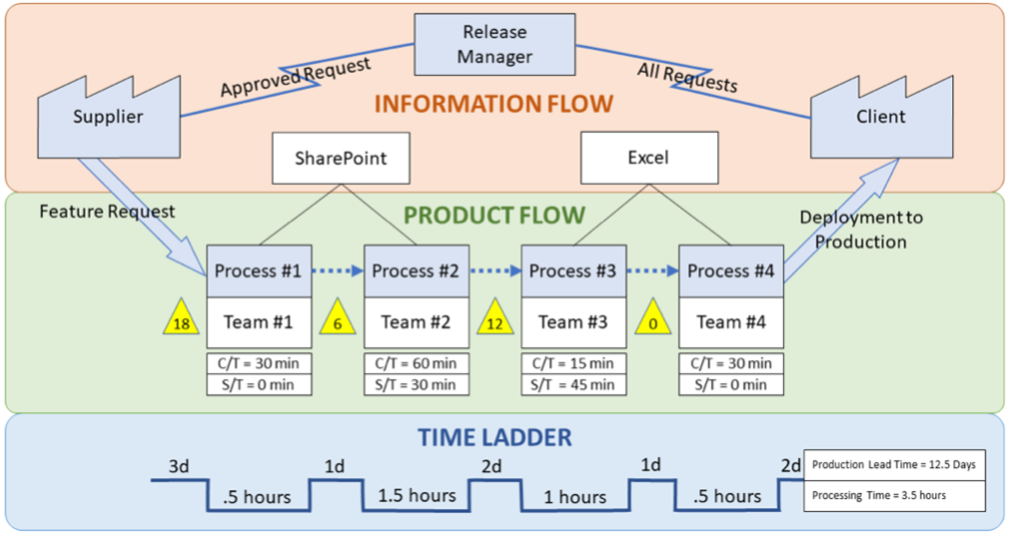
5. VALUE STREAM MAPPING:
Value-stream mapping is a lean-management method for analyzing the current state and designing a future state for the series of events that take a product or service from its beginning through to the customer with reduced lean wastes as compared to current map. A value stream focuses on areas of a firm that add value to a product or service, whereas a value chain refers to all of the activities within a company
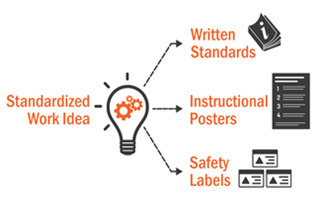
6. STANDARDIZED WORK:
Standardized work is one of the key components of a Just-in-Time production system. In order to achieve a balanced work flow, cycle time equal to Takt time, and high quality, work must be standardized at all operations for optimum efficiency and consistency.
7. AUTONOMATION ( JIDOKA ) :
Also referred to as “jidoka,” it’s described as “intelligent automation,” where the worker has the authority to stop the process when an abnormality occurs. It utilizes the following four quality control principles:
- Detect/find the abnormality
- Stop the process
- Fix or correct the abnormality
- Investigate the root cause and implement corrective action.
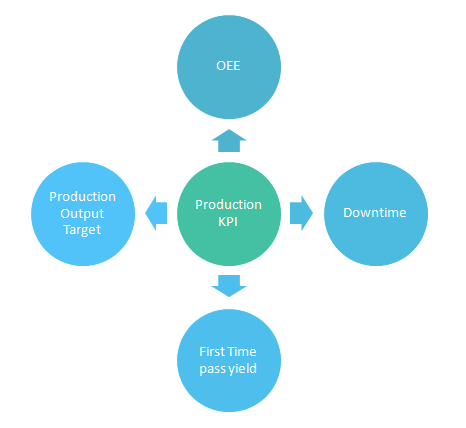
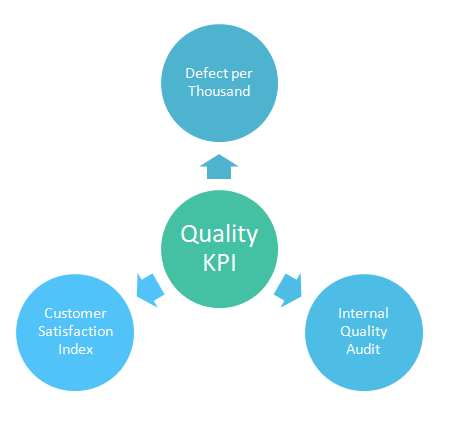
8.KPI (Key Performance Indicators):
A Key Performance Indicator is a measurable value that demonstrates how effectively a company is achieving key business objectives. Organizations use KPIs at multiple levels to evaluate their success at reaching targets. High-level KPIs may focus on the overall performance of the business, while low-level KPIs may focus on processes in departments such as Production,Quality , Warehouse , Maintenance ,sales, marketing, HR, support and others.
9.Six Big Losses
- Breakdown
- Startup time/Planned Downtime
- Small Stops
- Slow Speed of Machine
- Startup Reject
- Production Rejection